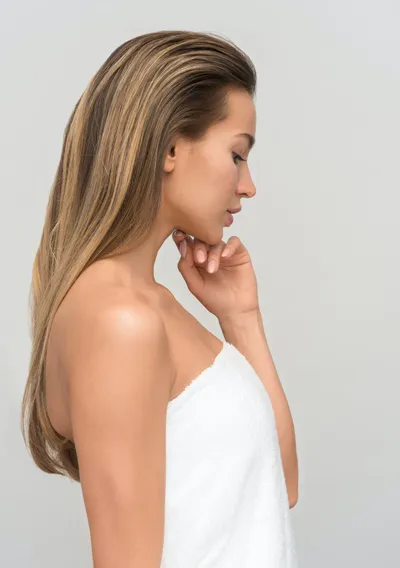
Bicalutamide's Roles In Scalp Hair Loss In Women

Bicalutamide (Generic for Casodex, Oral Tablet)
Bicalutamide was patented in 1982 and approved for medical use in 1995
Taken by mouth, bicalutamide (bica), sold under Casodex or similar, is an antiandrogen (NSAA).
It's popular as an off-label use for scalp hair loss for women.
Originally it was developed and is still primarily used to treat prostate cancer. It has a nonsteroidal chemical structure.
The drug is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.
It's the most widely used antiandrogen in the treatment of prostate cancer and has been prescribed to millions of men with the disease.
An Alternative To Spironolactone Or Cyproterone
Bicalutamide is considered to be an alternative drug for spironolactone (spiro) or cyproterone acetate (cypro).
 Bicalutamide's Roles In Scalp Hair Loss In Women
Bicalutamide's Roles In Scalp Hair Loss In WomenNo direct studies have been done to show which antiandrogen is better than the other.
At this point in time, any outside opinions about bica, spiro, or cypro are purely anecdotal.
When used under a hair restoration physician's advice, bicalutamide has shown great promise for addressing female pattern hair loss (FPHL).
This is especially true with combined with other supportive hair loss remedies.
Bicalutamide Combined With Minoxidil And Spironolactone
Oral bicalutamide is often combined with topical minoxidil and oral or topical spironolactone (spiro).
Some hair restoration experts will actually prescribe oral bicalutamide as an alternative to spironolactone.
Topical spironolactone, designed for addressing acne, is often mixed with science-backed ingredients like tretinoin, clindamycin, and tranexamic acid.
 Bicalutamide's Roles In Scalp Hair Loss In Women
Bicalutamide's Roles In Scalp Hair Loss In WomenDepending on hair restoration or other goals, oral bicalutamide (average dose of 50 mg) is combined with oral estradiol (4-8 mg) and taken daily.
Progesterone Cream May Be Added To The Combination
Progesterone may be added, possibly as a cream.
Women as young as their early to mid-30s suffering from androgenetic alopecia have been reported hair regrowth.
They have experienced significant hair regrowth after extended treatments with bicalutamide.
It works by selectively blocking the androgen receptor (AR).
This is the biological target of the androgen sex hormones testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Both hormones contribute to hair loss in women (and men).
Off-Label Treatments For Androgen-Dependent Hair Conditions
The drug is also employed for the off-label (non-approved) treatment of androgen-dependent skin and hair conditions.
These conditions include acne, seborrhea, excessive hair growth, and scalp hair loss in women.
It is also utilized for women experiencing high testosterone levels due to polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Bicalutamide may also be used to treat excessive hair growth and scalp hair loss in women as a component of feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women.
Estrogen-like Side Effect In Men
 Bicalutamide's Roles In Scalp Hair Loss In Women
Bicalutamide's Roles In Scalp Hair Loss In WomenBica does not lower androgen levels. The medication can have some estrogen-like effects in men when used as
monotherapy due to increased estradiol levels. Bicalutamide or Casodex is most likely prescribed to be taken at 25 to 50 mg/day, generally in combination with a birth control pill.
Bicalutamide May Harm An Unborn Baby
The drug which can be absorbed through the skin and lungs. Bicalutamide may harm an unborn baby if the biological parents conceive while on the drug.
Women who are pregnant or who may become pregnant should not handle Bicalutamide. Nor should they breathe the dust from the tablets.
Use effective birth control to prevent pregnancy while using Casodex and for at least 130 days (about 19 weeks) after your last dose.
The elimination half-life of the medication is around one week.
Liver Issues
Casodex can harm your liver. Bicalutamide has a small but unsubstantiated risk of causing full liver failure.
 Bicalutamide's Roles In Scalp Hair Loss In Women
Bicalutamide's Roles In Scalp Hair Loss In WomenCall your doctor at once if you have the following symptoms:
nausea, upper stomach pain, itching, loss of appetite, dark urine, clay-colored stools, or jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes).
Bicalutamide is well-absorbed, and its absorption is not affected by food.
It shows peripheral selectivity in animals but crosses the blood-brain barrier. It affects both the body and brain in humans.
Generic Versions Of Bicalutamide
Bicalutamide is available as a generic medication. The drug is sold in more than 80 countries, including most developed countries.
Side effects depend on the type and specific antiandrogen in question.
In general, antiandrogens are much better tolerated by women.
Antiandrogens that work only by directly blocking androgens have minimal side effects.
Estrogens are made from androgens in the body. Antiandrogens that suppress androgen production can trigger low estrogen levels.
Symptoms Of Low Estrogen Levels
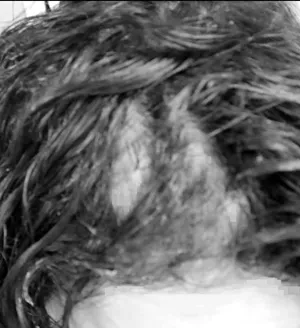
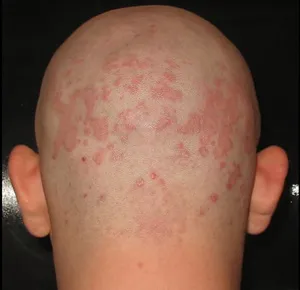
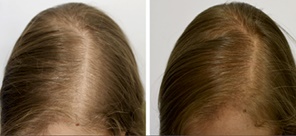 Improvement in scalp hair density in a 37-year-old woman treated with 25 mg/day bicalutamide monotherapy. Left is before treatment and right is after 6 months of therapy.
Improvement in scalp hair density in a 37-year-old woman treated with 25 mg/day bicalutamide monotherapy. Left is before treatment and right is after 6 months of therapy.This may cause associated symptoms like hot flashes, menstrual irregularities, and osteoporosis in premenopausal women.
It may also cause some weight gain, loss of energy, and bouts of tiredness. Some people claim it is helpful for overall mental health and clarity.
Common side effects in men include breast tenderness or enlargement, feminization, hot flashes, sexual dysfunction, infertility, and osteoporosis.
Best wishes to all.
Note: I am not a physician. The above blog was written for entertainment purposes. When considering consuming any of the medications listed above, see your primary care physician or your chosen hair restoration physician.Social Media Network Information
Please follow us on Twitter at: https://Twitter.com/HairBoutique. I look forward to meeting new people from all walks of Twitter and learning from their Tweets.