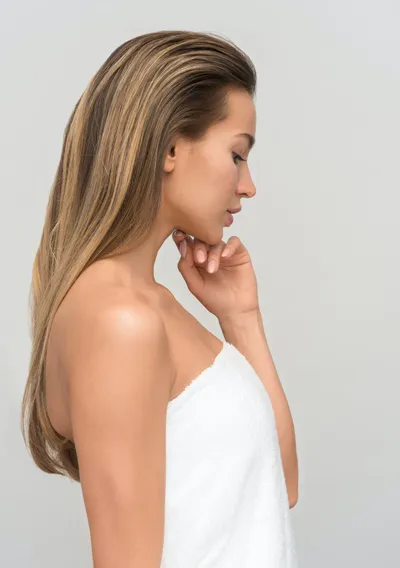
What's Old Is New Again In Women's Hair Loss
 Image by Apostolos Vamvourous - Unsplash.com
Image by Apostolos Vamvourous - Unsplash.comWhat's Been Used
Minoxidil was developed in the late 1950s by the Upjohn Company (Pfizer) to treat ulcers but proved ineffective.
Instead, it proved to be a potent antihypertensive vasodilator.
In 1963, studies resulted in the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approving the drug under the brand name Loniten to treat blood pressure.
Rogaine Was Approved By FDA As A Topical Hair Loss Solution In 1988
It was available as oral tablets starting in 1979 but had a side effect of growing hair. By the 1980s, Loniten was being prescribed off-label by physicians for their male patients with hair loss.
In August of 1988, the FDA approved the sale of the drug under the name of Rogaine for the treatment of (MPHL), male pattern hair loss (androgenetic alopecia).
Eventually, it became available as an oral tablet and a topical liquid or foam. It was ultimately approved as a medication used for the treatment of high blood pressure and both male and female pattern hair loss.
2% Topical Rogaine For Women, 5% For Men
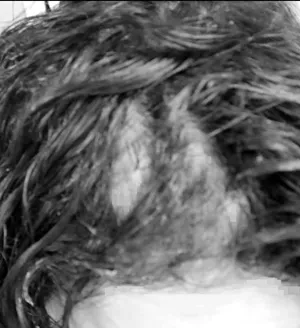
 Women's Hair Loss
Women's Hair LossAlthough initially not available for women, it was eventually recommended they use 2% minoxidil in a liquid topical formulation.
It was suggested men use the 5% formula available in topical foam.
Over time, women ignored the FDA recommendations and started to use the full strength 5% solution.
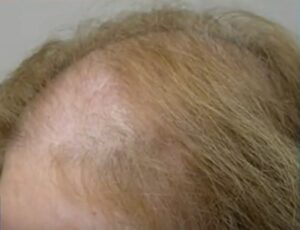
Women's Hair Loss Often Triggers Of Unrelenting Grief
 What's Old Is New Again In Women's Hair Loss - Isaiah McClean - Unsplash.com
What's Old Is New Again In Women's Hair Loss - Isaiah McClean - Unsplash.com "When women struggle with hair loss, it often triggers a unique type of deep sadness and grief" — Karen Marie Shelton, CEO/Founder of Hairboutique.com.
Sudden, progressive, or chronic hair loss can also trigger major ongoing stress and worry.
Ironically, some of the known triggers for various types of alopecia are extreme and/or chronic stress. The stress from hair loss perpetuates the cycle of hair loss by triggering additional shedding.
Science Is Getting Ahead Of Female Pattern Hair Loss
Science is breaking female hair loss barriers. It is getting ahead of female pattern hair loss with revolutionary new non-surgical treatments.
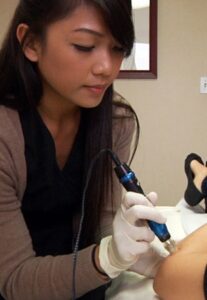 What's Old Is New Again In Women's Hair Loss - Collagen Induction Therapy - Wikipedia
What's Old Is New Again In Women's Hair Loss - Collagen Induction Therapy - WikipediaAlthough women are traditionally poor hair restoration surgical candidates, they are responding to other non-invasive treatments, which include but are not limited to the following type of treatments such as:
- jet peel scalp treatment (jets of air + liquids)
- scalp microneedling
- collagen induction therapy
- platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections
- low-level laser therapy (LLLT)
- scalp micropigmentation (SMP)
These revolutionary hair loss treatments are especially beneficial when combined appropriately and performed by a hair loss specialist such as a dermatologist or hair restoration surgeon.
Utilizing Oral + Topical Formulations Of Minoxidil With Other Formulations
 What's Old Is New Again In Women's Hair Loss- Photo - Jonn Leffmann
What's Old Is New Again In Women's Hair Loss- Photo - Jonn Leffmann Initially, women were not encouraged to utilize Minoxidil as a topical hair regrowth formula.
Eventually, the FDA approved a lower dose. Eventually, some female hair loss experts began recommending that women utilize the 5% topical solution.
As of 2022, some hair loss experts are compounding formulas together.
They are combining minoxidil and Propecia (finasteride) into customized topical solutions.
In some cases, the two hair loss drugs approved by the FDA are being prescribed as both tablets and topical lotions.
Rogaine Is Once Again Popular As An Oral Tablet
 What's Old Is New Again In Women's Hair Loss
What's Old Is New Again In Women's Hair LossYes, Rogaine is once again very popular in pill form, just as it was back in the late 1980s and early 1990s before lotions became more popular. Not only is it considered highly effective, but it is also considered less expensive than other formulas.
One of the know side effects of Propecia (finasteride) is that it may cause congenital birth defects for women of reproductive ages.
Some female hair loss experts instead prescribe a combination of birth control pills like Yaz and spironolactone to create a similar result to taking a more dangerous regiment of Propecia.
Besides prescribing "off-label" solutions, hair loss experts are also experimenting with custom dosages to avoid any possible side effects that higher dosages might trigger.
Women's Hair Loss Experts Are Optimistic
One side effect for women taking rogaine pills may experience hair growth throughout their entire body — as opposed to drops or foams applied topically to the scalp.
 Oral forms of rogaine can stimulate hair growth or what's called hypertrichosis on the temples and sideburns.
Oral forms of rogaine can stimulate hair growth or what's called hypertrichosis on the temples and sideburns.
Regardless, dermatologists are very optimistic about new ways to treat all types of hair loss for women. Most dermatologists believe that oral Rogaine is worth the risk of side effects.
Dr. Rodney Sinclair, an esteemed professor of dermatology at the University of Melbourne in Australia, reported in 2015 that low-dose minoxidil saw successful hair growth in 100 women.
Since then, Dr. Sinclair has treated 10,000 similar patients.
Summary
Until recently, women struggling with all types of hair loss, especially androgenetic alopecia (female pattern hair loss), have always taken a back seat to men struggling with hair loss.
Over the past few years, scientists, dermatologists, and hair loss specialists have focused on providing women with equal hair loss solutions and treatments.
Even though Rogaine is considered a very old hair loss formulation, what's old is new again in women's hair loss treatments. Rogaine has once again become popular as an oral tablet and part of different compounding topical formulations.
Disclaimer: This blog is not provided as medical advice. It is intended for informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Never ignore professional medical advice in seeking treatment because of something you have read on Hairboutique.com.
Social Media Network Information
Please follow us on Twitter at: https://Twitter.com/HairBoutique. I look forward to meeting new people from all walks of Twitter and learning from their Tweets.