Is Astaxanthin A Good Supplement For Women's Hair Loss?
 Astaxanthin Gel Cap
Astaxanthin Gel CapThe ketocarotenoid astaxanthin (ASX), 3,30-dihydroxy-b,b-carotene-4,40-dione, was originally isolated from a lobster by Kuhn and Sorensen.
Does Astaxanthin Hinder 5-Alpha-Reductase
Some laboratory studies have shown astaxanthin may hinder an enzyme called 5-alpha-reductase.
As a result, it could keep testosterone from changing into the hormone DHT in the body.
There is mounting evidence that astaxanthin (as-ta-zan-thin) possesses various health benefits.
It has important nutraceutical applications in the field of dermatology and hair loss.
Benefits Of Astaxanthin
When taken as a dietary supplement, its thought to have a range of potential mechanisms through which astaxanthin might exert its benefits on skin homeostasis.
 Astaxanthin Gel Cap
Astaxanthin Gel CapThese include photoprotective, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects.
Is It Synthetic Or Derived From H pluvialis?
The commercial production of this pigment has traditionally been performed by chemical synthesis.The microalga Haematococcus Pluvialis appears to be the most promising source for its industrial biological production.
 Astaxanthin Gel Cap
Astaxanthin Gel CapCurrently, 95% of ASX available in the market is produced synthetically using petrochemicals due to cost-efficiency for mass production.
Many petrochemicals are some of the most toxic substances known to man.
Safety issues have arisen regarding the use of synthetic ASX for human consumption, while the ASX derived from H. pluvialis is the main source for several human applications, including dietary supplements.
Because of its molecular structure, ASX has unique features that support its potential use in promoting human health. When it's not synthetic.
If you decide to take ASX supplements for your hair loss issues, make sure to read the labels closely. Verify that you are not taking synthetic formulas.
Can You Assimilate Supplements Successfully?
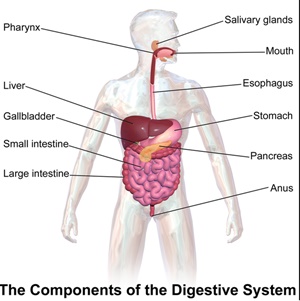
If the body's digestion is not functioning properly, any oral supplements to help slow hair loss and trigger regrowth may not be assimilated by the body.
This depends on a variety of health and physical conditions.
If digestion is sluggish, taking any type of hair loss nutraceuticals, even if organic and of the highest potency and freshness, may have minimal, if any, benefit.
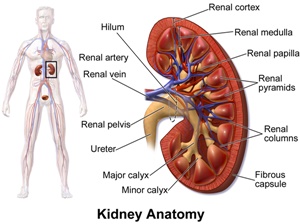
The same is true if the kidneys are not functioning properly.
If the kidneys are weak or malfunctioning, there may be a toxic build-up of this supplement that is not assimilated properly.
Are Your Supplements What You Think They Are?
 BruceBlaus. Blausen.com staff (2014). "Medical gallery of Blausen Medical 2014". WikiJournal of Medicine 1 (2). DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 2002-4436. - Own work
BruceBlaus. Blausen.com staff (2014). "Medical gallery of Blausen Medical 2014". WikiJournal of Medicine 1 (2). DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 2002-4436. - Own workSince all vitamin and nutrient supplements are not under the control and monitoring of the US FDA, there are no formal controls over the vitamin and supplement industry.
To save money, many manufacturers will import the ingredients for vitamin supplements from China and other countries.
Those ingredients may be tainted with toxic pesticides or other ingredients.
Bulk Vitamin And Herbal Ingredients May Be Toxic
 Henry Vandyke Carter - Henry Gray (1918) Anatomy of the Human Body (See "Book" section below) Bartleby.com: Gray's Anatomy,
Henry Vandyke Carter - Henry Gray (1918) Anatomy of the Human Body (See "Book" section below) Bartleby.com: Gray's Anatomy,Even still, it may take a long time for the bulk vitamins and herbs to arrive in the United States.
By the time they arrive, they may no longer be viable for consumption.
When if toxic and no longer viable, if the ingredients are still manufactured, they may sit in warehouses or on store shelves for many months, if not years.
By that point, the supplements may be no better than sawdust. If anything, they present a toxic source for your body to eliminate.
There would be little if any, value. If anything, they may do more harm than good, adding to the existing toxic overload in the system.
Astaxanthin Contains A Powerful Antioxidant
 It's referred to as “Super Vitamin E”. It appears to outperform vitamins C, E, and other carotenoids.
It's referred to as “Super Vitamin E”. It appears to outperform vitamins C, E, and other carotenoids. The carotenoid is found in microalgae.
It's been scientifically proven to pack a heftier free radical-fighting punch than other antioxidants. That includes vitamin E, green tea, and coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10).
It’s considered 6,000 times stronger than vitamin C. It's thought to be the holy grail of antioxidants in neutralizing harmful singlet oxidation.
Summary - Does Astaxanthin Regrow Hair?
Astaxanthin, a xanthophyll carotenoid, is a secondary metabolite. It's naturally synthesized by a number of bacteria, microalgae, and yeasts.
When 10 to 12 mg are taken daily, ASX is thought to increase hair growth by up to 22%. It's thought to curb production of the follicle-damaging hormone DHT.
There are many other factors to consider when taking this supplement for hair loss issues.
1. Is the Axtaxanthin synthetically produced, which may be highly toxic?
2. Is it derived from H. pluvialis?3. Can the digestion and kidneys assimilate the benefits of Astaxanthin?
4. Do they build up in the body?5. How healthy are all the other body organs?
6. Is the supplement source of the highest quality?7. Is it organic, grown natively, and of the highest integrity?
8. Or is it tainted by pesticides or other toxins from oversea sources?Astaxanthin may hinder 5-alpha-reductase. It may prevent conversion of testosterone into DHT. It may also increase hair growth by up to 22%.
But only if all other factors are optimal. While it may offer hair loss benefits for women, it also may be nothing more than toxins for the body to release
Only you can decide what are the risks versus the rewards.
Best wishes to all.Social Media Network Information
Please follow us on Twitter at: https://Twitter.com/HairBoutique. I look forward to meeting new people from all walks of Twitter and learning from their Tweets.